음수법과 체위 변화로 관찰된 만성 췌장염과 가성낭종
Visible Chronic Pancreatitis and Pseudocyst after Drinking Water and Changing Position
Article information
Abstract
60세 여자 환자가 상복통으로 방문 후 복부 초음파 검사를 시행하였다. 복부 초음파상 췌장머리 부위에 췌장석회화가 관찰되었고 췌장꼬리 부위 관찰이 어려워서 반우위 및 음수법을 시행하였다. 췌장꼬리 부위에 2.5 cm 크기의 경계가 명확한 저에코의 낭성 병변이 관찰되었다. 추가 CT 또는 MRI를 촬영하여 만성 췌장염과 가성낭종으로 진단하였다. 초음파가 췌장을 보는데 일부 제한점이 있으나 음수법, 반우위 혹은 반좌위 등 자세 변경 및 압박법 등을 사용하면 전체 췌장 관찰 및 질환을 찾는 데 많은 도움이 된다.
Trans Abstract
Chronic pancreatitis represents the result of a continuous, prolonged, inflammatory, and fibrosing process that affects the pancreas. Pseudocysts are common sequelae of acute pancreatitis or chronic pancreatitis and the most common cystic lesion of the pancreas. Abdominal ultrasonography is limited in detecting pancreatic disease, especially that located in the pancreatic tail. A 60-year-old woman presented to our institute with upper abdominal discomfort. We visualized pancreatic calcification and pseudocyst after filling the stomach with water by drinking and changing her body position. The patient was diagnosed with chronic pancreatitis and pseudocyst of the pancreatic tail.
서 론
만성 췌장염은 무증상으로부터 복통에 이르기까지 다양한 증상이 나타날 수 있으며 췌장석회화, 당뇨병, 지방변이 특징이다. 가성낭종은 급성 췌장염이나 만성 췌장염의 흔한 후유증으로 췌장의 가장 흔한 낭성 병변이다. 복부 영상 검사에서 만성 췌장염은 췌장 실질 및 췌관 변화로 진단할 수 있다. 가성낭종은 벽을 가지고 타원형 또는 원형의 액체로 채워져 있으며 한개 혹은 여러 개일 수 있다. 복부 초음파 검사는 췌장 질환, 특히 꼬리를 감지하기 어렵다. 저자들은 60세 여자가 상복부 통증으로 내원하여 초음파 검사상 음수법과 반우위로 자세 변경 후 만성 췌장염 및 췌장 꼬리 부위에서 2.5 cm의 비교적 경계가 뚜렷한 가성낭종을 발견하였다. 추가적인 전산화단층촬영(computer tomography, CT)과 자기공명영상(magnetic resonance imaging, MRI)을 통하여 만성 췌장염과 가성낭종으로 진단한 예를 보고한다.
증 례
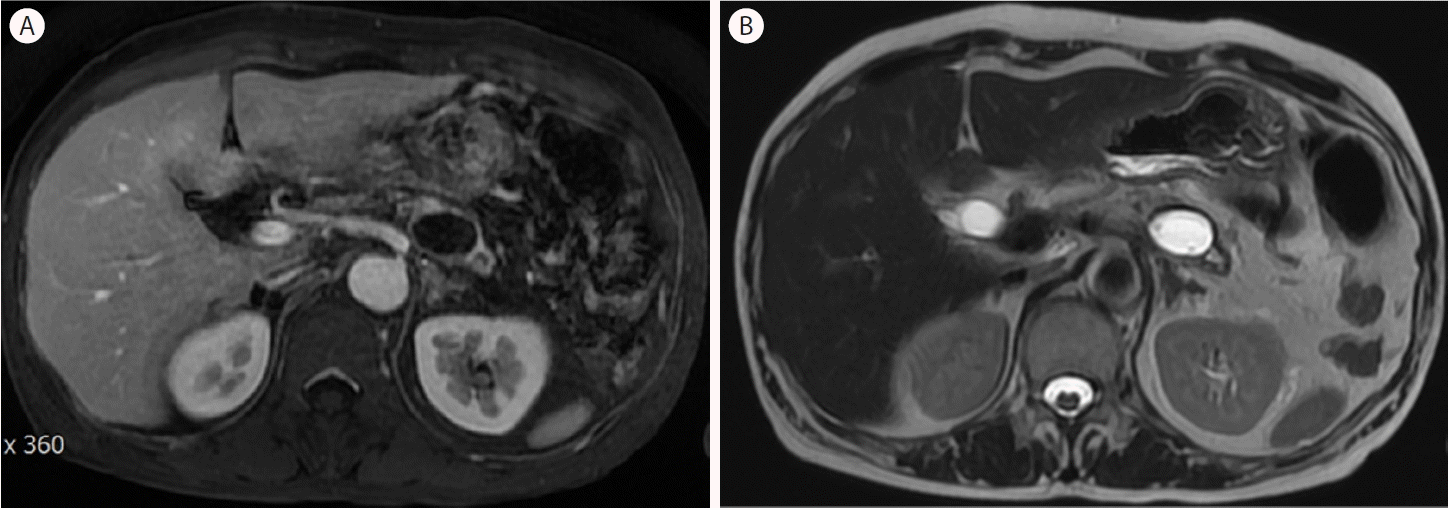
60세 여자가 수일간의 상복부 복통으로 방문하였다. 이전 만성 췌장염 병력이 있고 당뇨병이 있었다. 술은 주 4회 소주 한 병씩 마시고 흡연력은 없었다. 상복부 복통이 있었지만 압통은 없었다. 활력징후는 혈압 135/80 mmHg, 맥박 분당 70회, 호흡 분당 16회, 체온 37.0℃였다. 백혈구 10,300/mm3, 혈색소 11.3 g/dL, 혈소판 431,000/mm3, AST/ALT 57/20 U/L, ALP/γGTP 150/90 U/L, 총빌리루빈 0.8 mg/dL, amylase/lipase 130/150 U/L, BUN/Cr 20/1.1 mg/dL, HBs Ag/Ab (-/+), HCV Ab (-), Ca 19-9 15.9 U/mL였다. 키는 154 cm, 몸무게는 55 kg이었다. 복부 초음파상 췌장머리 부위에 췌장석회화가 의심되었고 Doppler 초음파에서 췌장석회화를 시사하는 twinkling artifact가 관찰되었다(Fig. 1). 장가스로 췌장꼬리 부위 관찰이 어려워서 반우위 및 음수법을 시행하였다. 일반 생수 400 mL 가량 마시게 한 후 췌장꼬리 부위에 2.5 cm 크기의 경계가 명확한 저에코의 낭성 병변을 관찰할 수 있었다(Fig. 2). CT상 췌장머리에 다발성의 췌장석회화와 췌장꼬리에 크기 2.5 cm의 조영증강되지 않는 낭성 질환이 관찰되었다(Fig. 3). T1강조 MRI에서 췌장꼬리에 조영되지 않는 저신호의 낭성 병변, T2강조 MRI에서 췌장꼬리에 고신호의 낭성 병변인 가성낭종으로 진단되었다(Fig. 4). 췌장 효소 제제와 비마약성 진통제등 약물 치료를 시작하였고 복통이 호전되었고 가성낭종에 의한 증상이 악화되지 않아 퇴원 후 외래에서 추적 관찰 중이다.
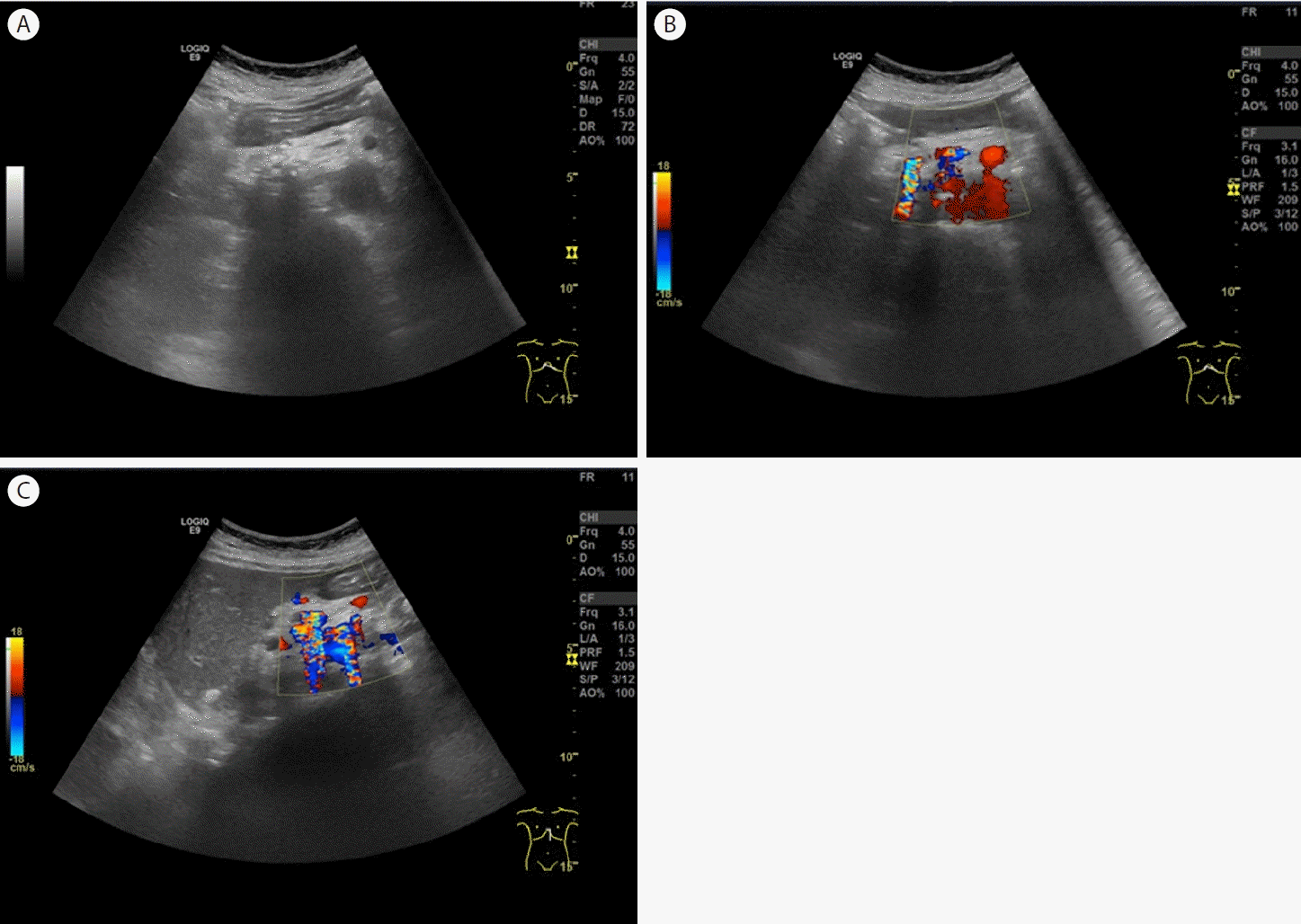
Ultrasonography of the pancreatic calcification. (A) Transverse scan shows pancreatic calcification and dilatation of the main pancreatic duct. (B) Color Doppler ultrasound (transverse scan) shows a twinkling artifact caused by pancreatic calcification. (C) Color Doppler ultrasound (longitudinal scan) shows a twinkling artifact caused by pancreatic calcification.
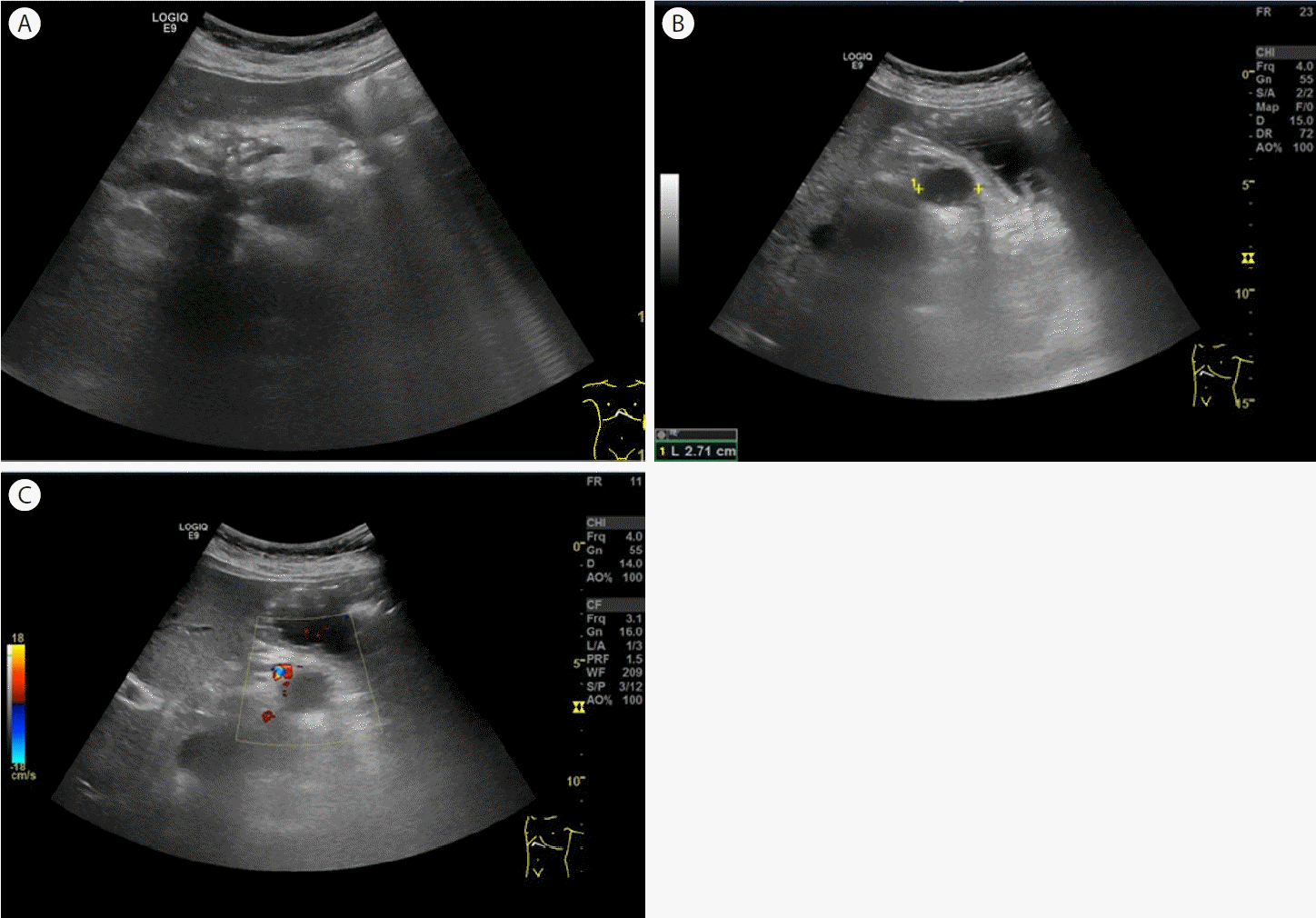
Ultrasonography of the pseudocyst. (A) Transverse scan does not show the pancreatic tail lesion because of the presence of gas. (B) Transverse scan shows a 2.5 cm oval, hypoechoic lesion in the pancreatic tail after drinking water and moving into the right lateral decubitus position. (C) Color Doppler ultrasound shows no vascularity.

Computed tomography (CT). (A) CT shows multiple calcifications in the pancreatic head. (B) CT shows a round cystic lesion in the pancreatic tail.
고 찰
만성 췌장염 증후군은 주로 만성적인 음주로 인한 반복적인 췌장 손상으로 인해 발생하며, 임상적으로 췌장 외분비 및 내분비 기능 이상과 영상학적으로 관찰 가능한 췌장 구조의 변화를 특징으로 한다. 그러나 많은 임상적 특징이 나타나기까지 시간이 걸리며 만성 췌장염의 초기 단계에서는 나타나지 않을 수 있다. 복부 초음파 소견으로는 췌장석회화가 가장 특이적인 소견이며 그 외에 췌관의 불규칙한 확장, 췌장 실질의 불규칙한 변연과 소엽성 모양, 췌장 실질의 비균일적인 에코 양상, 췌장 가성낭종 등이 있다. 만성 췌장염의 췌장 실질 혹은 췌관의 석회화를 관찰하는 것이 중요한데 color Doppler 초음파에서 췌장석회화를 시사하는 twinkling artifact가 관찰하는 것이 도움이 되고 본 증례에서도 이용되었다.
가성낭종은 급성 혹은 만성 췌장염의 합병증으로 벽을 가지고 타원형 또는 원형의 액체로 채워져 있으며 한 개 혹은 여러 개일 수 있다. 초음파상 췌장 혹은 췌장 주위에 무에코 혹은 저에코의 액체로 나타나며 저에코 혹은 고에코의 debris를 동반 가능하다. 췌장 가성낭종의 진단은 일반적으로 만성 췌장염의 병력이 있는 환자 또는 급성 췌장염에서 회복된 환자의 영상 촬영에서 췌장 내 또는 췌장 주변의 캡슐화된 체액 수집을 발견함으로써 이루어진다. 가성낭종은 복부 초음파에서 볼 수 있지만 일반적으로 진단을 확인하기 위해 추가로 조영제 CT 또는 MRI를 촬영하면 비교적 정확히 진단할 수 있다. 진단이 불확실한 경우 임상적 상황이 불분명하거나 영상 소견이 비정형인 경우 체액 채취 및 낭종벽 조직 검사를 위한 내시경 초음파를 시행할 수 있다[1]. 가성낭종은 지속적인 복통, 구역, 구토, 조기 포만감, 식욕 저하, 체중 감소, 황달과 같은 증상이 있거나 감염, 출혈, 장관 폐쇄 혹은 담도 폐쇄 같은 합병증 동반된 경우 배액술을 시행한다[2].
초음파 스캔 시 방해되는 인자들은 위장관 내 가스, 심한 비만, 수술 창, 바륨 조영술이 있다[3]. 췌장꼬리 부위는 초음파의 가장 취약한 부분으로 통상의 방법으로 관찰이 어렵다. 압박법은 위에 가스가 많아서 췌장이 잘 안보일 때 탐촉자로 복부를 점진적으로 압박하여 위의 가스를 밀어내면 췌장이 더 잘 보이고 자세 변경은 누워서 췌장 스캔 시 췌장이 잘 안보이면 반좌위, 반우위로 스캔하면 췌장이 더 잘 보인다[4]. 본 증례에서는 음수법 및 반우위의 췌위 변화를 동시에 사용하여 췌장꼬리 부위의 가성낭종을 관찰할 수 있었다. 음수법은 위에 300-500 mL의 물을 먹이고 5분 내지 10분 정도 앉힌 후 검사하면 췌장이 더 잘 보이는 경우가 많다[3]. 일반적으로 사용하는 물은 탈기수를 쓰지만 탈기수가 아닌 물을 사용해도 음창 확보에는 큰 차이가 없다고 알려져 있고 본 증례에서도 일반 생수로 췌장이 충분히 관찰되었다.
복부 초음파는 간편하고 실시간으로 정보를 얻을 수 있으나 민감도가 낮고 검사자에 대한 의존도가 높다. 특히 췌장꼬리 부위의 관찰은 쉽지 않다. 췌장 관찰을 위해 음수법, 체위 변화가 도움이 되며 전체 관찰을 위해 노력하여야 한다. 또한 다른 복부 영상 검사의 장단점을 알고 추가 검사도 충분히 고려하여야 한다.