갑상선결절로 오인된 Zenker씨 게실 1예
요약
갑상선결절을 주소로 세침흡인세포 검사를 위해 내원한 49세 여자 환자에서 갑상선 초음파 검사를 통하여 Zenker씨 게실을 의심하고 식도조영술을 통해 확진한 증례를 경험하였다. 시간이 경과한 후 시행한 초음파 검사에서 이전과 병변의 모양이 다를 경우, 연하운동에 따라 병변의 모양이 달라지거나 고에코의 띠모양의 병변과 여운현상 등이 보일 경우는 Zenker씨 게실을 의심하고 세침흡인세포 검사를 시행하지 말아야 한다.
중심 단어: 식도게실; 초음파; 갑상선결절
Abstract
The Zenker’s diverticulum is the most common diverticulum of the esophagus. It commonly occurs at the pharyngoesophageal junction that can appear in proximity to the thyroid gland. The food remnants or gas bubbles present in the diverticulum may mimic microcalcifications presented in papillary thyroid carcinoma on ultrasonography. Therefore, it is important to be able to differentiate between Zenker’s diverticulum and malignant thyroid nodule. The author reported a case of Zenker’s diverticulum mimicking a thyroid nodule in thyroid ultrasonography.
Keywords: Esophageal diverticulum; Ultrasonography; Thyroid nodule
서 론
Zenker씨 게실은 식도게실 중 가장 흔하며[ 1], 하부인두와 상부 식도 접합부에서 상부식도괄약근 기능의 이상으로 발생한다[ 2]. 식도게실은 주로 고령의 환자에서 연하장애 음식물의 역류, 만성기침 혹은 흡인과 같은 증상으로 발견되는 경우가 대부분이나, 식도조영술 검사에서 우연히 발견되기도 하고, 건강검진에서 갑상선 초음파 검사가 보편화되어 초음파 검사에서 Zenker씨 게실이 갑상선결절로 오인되어 발견되기도 한다[ 3- 5]. 식도게실의 초음파 양상이 갑상선암의 초음파 소견과 중복되는 점이 많아 실제 세침흡인세포 검사를 시행받은 경우도 보고되어 있다[ 6- 9]. 저자는 갑상선결절을 주소로 내원한 환자에서 식도게실의 특징적인 초음파 소견을 보여, 식도조영술을 통해 식도게실을 진단한 증례를 경험하였기에 문헌고찰과 함께 보고하는 바이다.
증 례
49세 여자 환자가 갑상선결절을 주소로 내원하였다. 환자는 내원 1주 전 시행한 건강검진 결과 갑상선 초음파 검사에 갑상선결절이 발견되어, 세침흡인세포 검사를 위해 방문하였다. 갑상선 질환의 과거력은 없었고, 이학적 검사 결과 특이 소견은 관찰되지 않았다. 외부 병원에서 시행한 갑상선 초음파 검사에서는 갑상선 좌하엽 부위에 1.28 × 0.78 cm 크기의 Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System 4 (K-TIRADS 4, 중간 의심)의 고형 우세 결절이 관찰되었으며, 결절 내부에 다발성의 점상 석회화가 관찰되었다( Fig. 1). 그러나 세포흡입세포 검사를 위해 본원에서 시행한 초음파 검사에서 개인의원에서 시행한 초음파 소견과는 달리 갑상선 아래 부위에 밝은 에코 띠 모양과 여운현상(ring-down artifact)을 보이는 Zenker씨 게실이 의심되는 소견이 관찰되었다( Fig. 2). 식도조영술 검사 결과, 상부식도 후방 부위로 Zenker씨 게실에 바륨이 차있는 모습이 확인되었다( Fig. 3). 환자는 별다른 증상이 없어 경과 관찰하기로 하였다.
고 찰
Zenker씨 게실은 1877년에 처음 Zenker와 von Ziemssen이 23예의 하인두게실을 보고한 이후, 전체 식도조영술의 약 1% 정도에서 발견되는 식도의 가장 흔한 게실이다[ 10]. 진성 게실은 장벽이 모두 포함되어 이탈되는데 반해, Zenker씨 게실은 식도의 근육층을 관통해 점막과 점막하층만 이탈하여 발생하는 가성 게실이며, 대부분 병변은 갑상선 좌엽 후방에 위치하며[ 1, 3, 10- 12], 드물게 갑상선 우하측에서 발견되기도 한다[ 13]. Zenker씨 게실의 특징적인 초음파 소견은 에코 발생도가 높으며 저에코의 변연부를 보이고, 병변의 내부에 고에코성 병변은 게실 내부의 공기 때문이며, 석회화와는 다르게 깨끗하지 못한 음향 그림자(acoustic shadowing)나 여운현상을 보인다. Walts와 Braunstein [ 6]은 초음파 검사로 Zenker씨 게실을 진단하는 데 도움이 되는 단서를 다음과 같이 1) 초음파 검사 중 환자의 위치를 바꾸거나 탐촉자로 게실 부위를 압박할 때 병변 부위의 변화, 2) 병변 내 공기 액체층(air-fluid level)이 있거나, 3) 삼킬 때 내용물의 움직임, 4) 반복 검사에서 병변의 초음파학적 모양의 변화가 있을 때, 5) 결절의 경계 내 소화관을 암시하는 다층 구조가 존재할 때로 제안하였다. DeFriend와 Dubbins [ 14]도 환자에게 물을 삼키게 하여 갑상선결절의 크기와 결절의 내부 에코 변화를 관찰함으로써 Zenker씨 게실의 진단에 이용하였으며, Komatsu 등[ 3]도 시간적인 차이를 두고 결절을 관찰하면 결절의 모양이 변하는 것이 진단에 도움이 된다고 하였다. 본 증례에서도 개인의원에서의 초음파 영상에서는 갑상선결절 모양의 종양성 병변이 관찰되었으나, 본원에서의 초음파 영상에서는 결절성 병변도 관찰되지 않았으며, 이전에 보이지 않던 여운현상이 관찰되어 시간에 따라 병변의 모양이 달라진 것이 진단에 도움이 되었다. 식도게실은 임상에서 갑상선 초음파 검사 상 갑상선결절로 오인할 수도 있으나, 물을 삼키거나 침을 삼킬 때 연하운동에 따른 결절 모양의 병변 내부 물질의 움직임과 이에 따른 에코의 변화를 관찰하고, 고에코성 띠모양의 병변과 동반되는 음향 그림자를 석회화 결절로 오인하지 않으면 감별진단에 큰 어려움이 없을 것으로 생각한다. 특별한 증상이 없는 Zenker씨 게실은 관찰만으로 충분하고 증상을 초래하는 경우에는 수술적 치료를 한다. 본 증례도 특별한 증상이 없어 경과 관찰하기로 하였다.
Figure 1.
Thyroid ultrasound in transverse view (A) and longitudinal view (B) showed a 1.28 × 0.78 cm sized predominant solid nodule (arrow) with multiple micro- and macrocalcification at the left lower lobe of the thyroid gland. 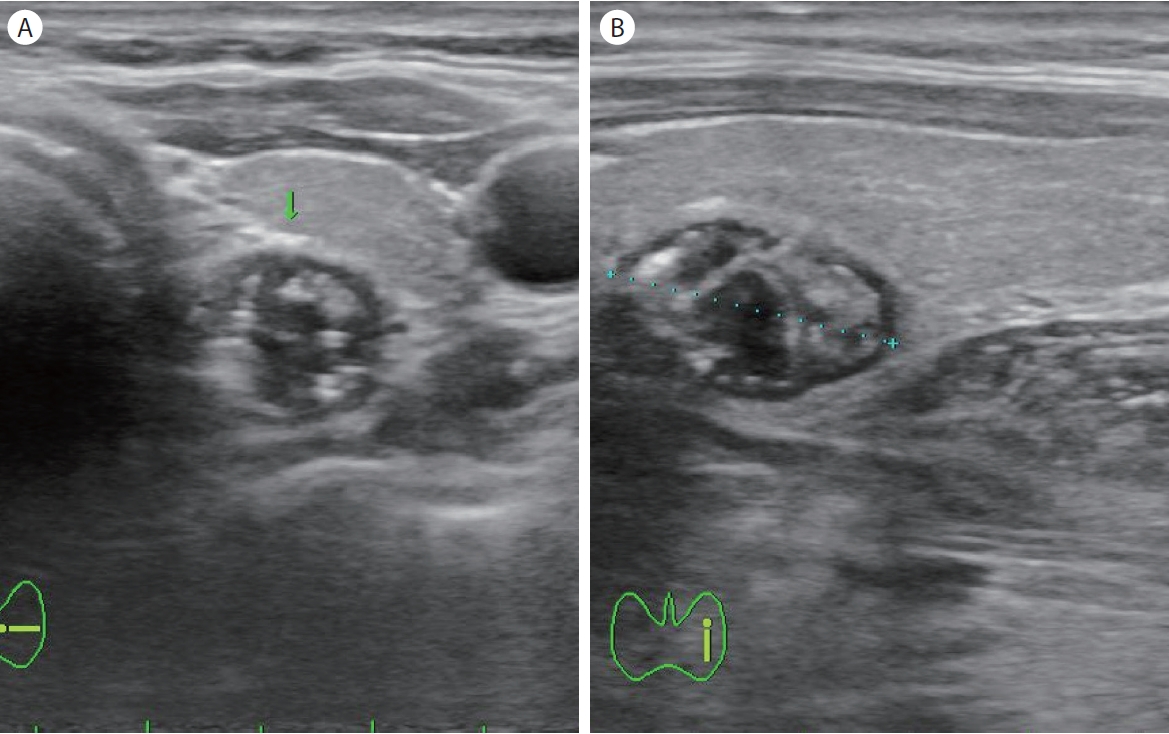
Figure 2.
Thyroid ultrasound in transverse view showed a bright white echo structure with a ring-down artifact at the below-left thyroid gland. Arrow: ring-down artifact suggests air shadowing. 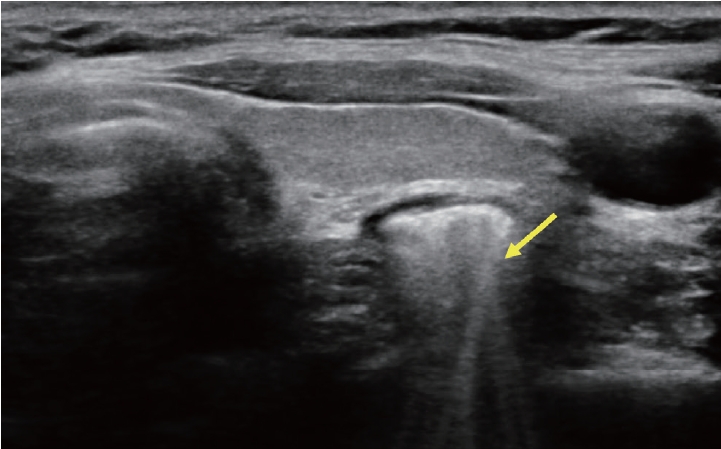
Figure 3.
The esophagography confirms a barium-filled sac projecting from the upper esophagus, posterior aspects. Arrow: Zenker's diverticulum. 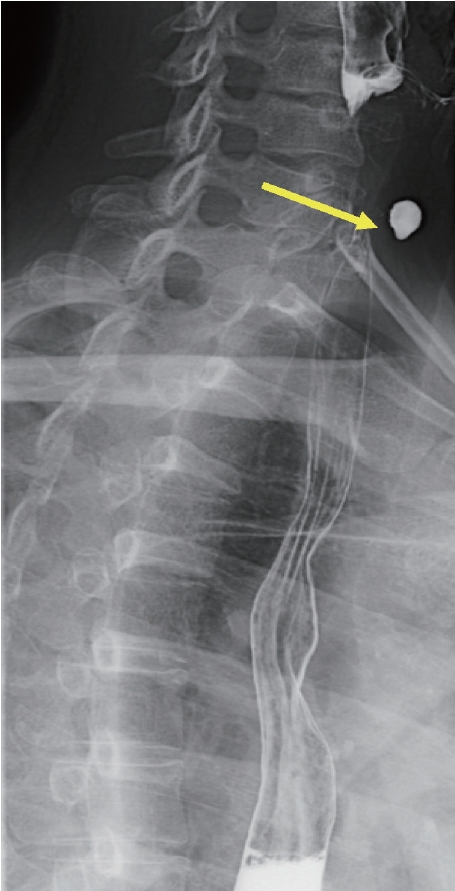
REFERENCES
2. Ekberg O, Nylander G. Lateral diverticula from the pharyngo-esophageal junction area. Radiology 1983;146:117–122.   3. Komatsu M, Komatsu T, Inove K. Ultrasonography of Zenker’s diverticulum: special reference to differential diagnosis from thyroid nodules. Eur J Ultrasound 2000;11:123–125.   5. Lixin J, Bing H, Zhigang W, Binghui Z. Sonographic diagnosis features of Zenker diverticulum. Eur J Radiol 2011;80:e13–e19.   6. Walts AE, Braunstein G. Fine-needle aspiration of a paraesophageal diverticulum masquerading as a thyroid nodule. Diagn Cytopathol 2006;34:843–845.   7. Shanker BA, Davidov T, Young J, Chang EI, Trooskin SZ. Zenker’s diverticulum presenting as a thyroid nodule. Thyroid 2010;20:439–440.   8. Oertel YC, Khedmati F, Bernanke AD. Esophageal diverticulum presenting as a thyroid nodule and diagnosed on fine-needle aspiration. Thyroid 2009;19:1121–1123.   9. Kim JH, Choi YS, Kim BK, Lee JS, Park YH, Hur B. Zenker's diverticulum suspected to be a thyroid nodule diagnosed on fine needle aspiration: a case report. J Med Cases 2012;4:261–263.  10. Jeyarajah R, Harford W. Diverticula of the hypopharynx, esophagus, stomach, jejunum, and ileum. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Sleisenger MH, eds. Sleisenger & Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology Diagnosis Management. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2002:359-361.
11. Kim J, Kim YJ, Kim EK, Park CS. Incidentally found pharyngoesophageal diverticulum on ultrasonography. Yonsei Med J 2002;43:271–273.   12. Yahara T, Machi J. Image of the month. Zenker diverticulum. Arch Surg 2002;137:619–620.  13. Choi CW, Ahn HY. A case of Zenker’s diverticulum mimicking a right side thyroid nodule. Int J Thyroidol 2018;11:56–59.   14. DeFriend DE, Dubbins PA. Sonographic demonstration of a pharyngoesophageal diverticulum. J Clin Ultrasound 2000;28:485–487.  
|
|